While and Do-While Loops
The other, if not the most, fundamental structure in programming are loops. A loop checks a condition and executes the body, then rechecks and executes the body, until the condition is false. Each time the loop executes the body is call an iteration. The loop will iterate until the condition is false.
While Loops
While loops are the simplest form of loops. Per the name, while loops iterate while their conditions are true and until they are false. Once the condition is false, the loop exits and moves on to the next code.
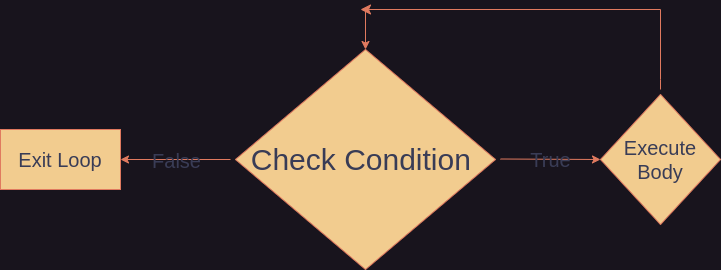 The flow of a while loop
The flow of a while loop
For example:
while(True):
print("true")
This code is an infinite loop. It will iterate and print "true forever, since the condition is never false. Not very useful. Let's try a while loop with a changing condition.
Loops are necessary for developing a process that require doing the same action multiple times. Like printing. Say I want to print every number from 0 to 1. I can do this with a while loop.
n = 0
while(n <= 10):
print(n)
n += 1
This script:
- Assigns n to the integer 0.
- Begins a loop that will execute until n is 10.
- Prints n.
- Increments n by 1.
- Repeats until n is 10.
Let's try another example: Say I want to write a program that prints every multiple of 2 from 2 to 20. We can do this with a while loop.
n = 2
f = 1
while(n * f <= 20):
print(n * f)
f += 1
Another way to accomplish this to to simply check if a number is even, since all multiples of 2 are by definition even. This code takes advantage of the modulo operator and an *if * statement.
n = 1
while(n <= 20):
if ( n % 2 == 0 ):
print(n)
n += 1
This code checks every number form 1 to 20. If the number is divisible by 2 it prints, if not nothing happens and the next number is checked.
Continue and Break
Python supports two keywords that allows us to stop a loop from iterating again or command a loop to jump to the next iteration.
Break
The break keyword causes a loop to immediately exit. break statements should be used only when necessary as when using them instead to end a loop instead of allowing the loop to end naturally based on its conditions can be considered bad style. However while loop utilizing break is often used to accept user input.
while (True):
meals = int(input("How many meals did you eat today?\n"))
if meals >= 0:
break
if (meals == 0):
print("You should eat something today!")
else:
print(meals," meals sounds ok.")
This code utilizes an infinite while loop. The loop will iterate and ask the user a question over and over until the number they provide is positive. If they give a positive number, the loop breaks. This is to ensure the user provides usable information.
The next section will cover the more widely applicable and succinct looping structure, the for loop.